
Those bonds are thus listed as liabilities on the company’s balance sheet. And the difference between how much it owns and how much it owes is called owners’ equity. That’s the amount the owners of the company (i.e. shareholders) have invested in the company. Clear Lake Sporting Goods has accounts payable and has collected payments from a few customers that it hasn’t yet shipped its product to (unearned revenue).

Short term debt
They’re recorded in the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet. Debtors and creditors can be individuals or businesses. Individuals and companies are typically debtors who borrow money from banks or other financial institutions.
Non-Current (Long-Term) Liabilities
Those liabilities coming due sooner—current liabilities—are listed first on the balance sheet, followed by long-term liabilities. The balance sheet is indeed a very helpful financial statement, but it also poses challenges. First, assets on the balance sheet, under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), are recorded at historical cost.
Other Definitions of Liability
Companies of all sizes finance part of their ongoing long-term operations by issuing bonds that are essentially loans from each party that purchases the bonds. This line item is in constant flux as bonds are issued, mature, or called back by the issuer. The outstanding money that the restaurant owes to its wine supplier is considered a liability. The wine supplier considers the money it is owed to be an asset. So on a balance sheet, accumulated depreciation is subtracted from the value of the fixed asset.
Trade debtors
- A company might take out debt to expand and grow its business or an individual may take out a mortgage to purchase a home.
- Most companies will have these two-line items on their balance sheets because they’re part of ongoing current and long-term operations.
- As debt repayments are made, the loan liability will decrease.
- Comparing several years of a company’s balance sheet may highlight trends, for better or worse.
- She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more.
The bank can take possession of the property through foreclosure and sell it to recoup the money owed if Sal defaults on the mortgage. A creditor may also take a debtor to court for failure to pay and this can lead to liens or encumbrances. Below represents the effect on the balance sheet for year 1 on a four-year loan of 100. The loan has straight-line repayment and an interest rate of 5% on beginning balance. These classifications are called private debt (borrowing from banks) and public debt (borrowing from capital markets). Secured debt is backed by collateral, usually in the form of an asset or group of assets.
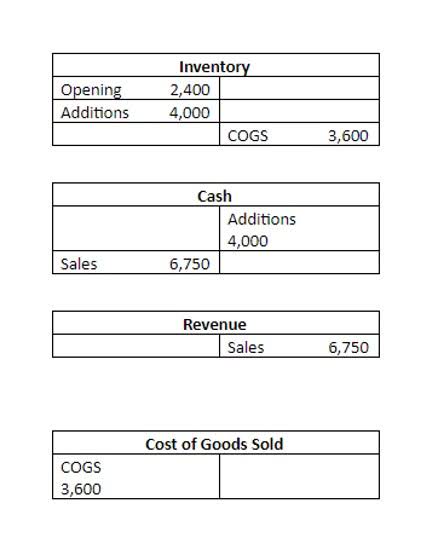
Example of Liabilities
If it does, it may be simple goods it uses to help deliver its service. For example, a cleaning company may keep an inventory of cleaning supplies. AT&T clearly defines its bank debt that’s maturing in less than one year under current liabilities. This the debt a firm owes to others is called a(n) is often used as operating capital for day-to-day operations by a company of this size rather than funding larger items which would be better suited using long-term debt. The court can send debtors to jail for unpaid child support in some cases.
- Land remains at historical cost, and depreciable items like buildings are reflected at their current book value (historical cost less accumulated depreciation).
- Except for land, fixed assets wear out and become outdated over time.
- In small business accounting, liabilities are existing debts that your business owes to another business, organization, vendor, employee, or government agency.
- In other words, the key is in determining what you are paying for and what purpose it serves.


Comment closed!